RESEARCH
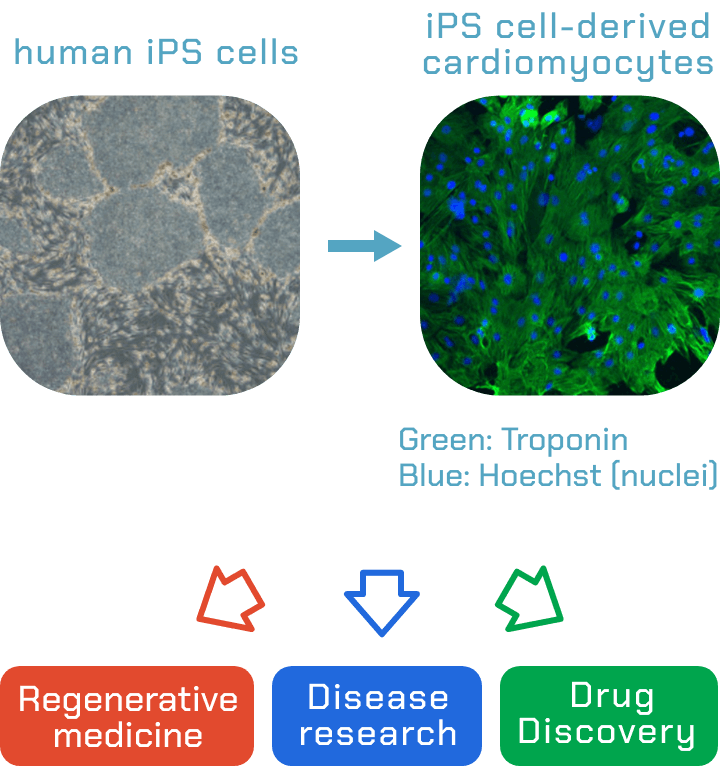
Our lab uses iPS cells to study cardiac cells with application towards regenerative medicine, drug discovery, and disease modeling.
Currently, we are working on four themes: (1) Development of myocardial regenerative medicine, (2) Disease-specific iPS cells , (3) Generation of mature cardiac cells for clinical application , and (4) Investigation into mechanisms determining the differentiation capacity of ES/iPS cells.
If you are interested, please get in touch with us.
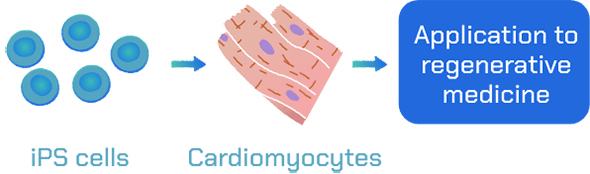
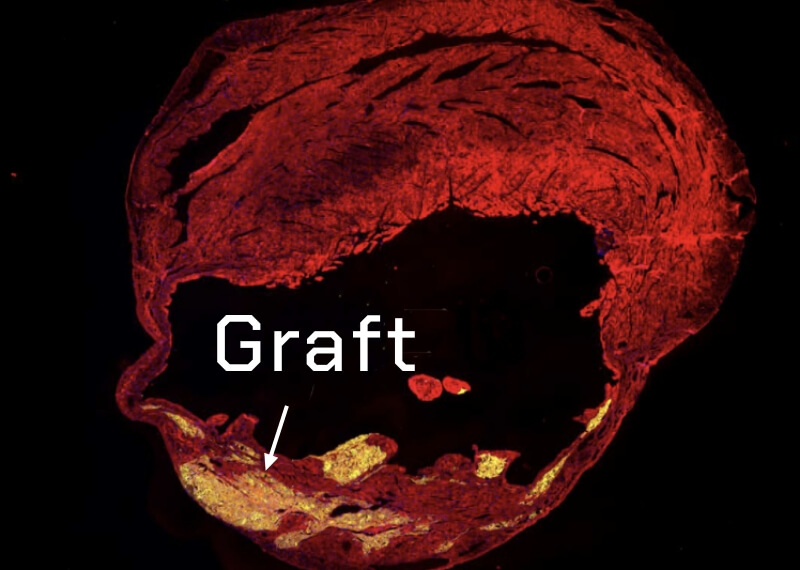
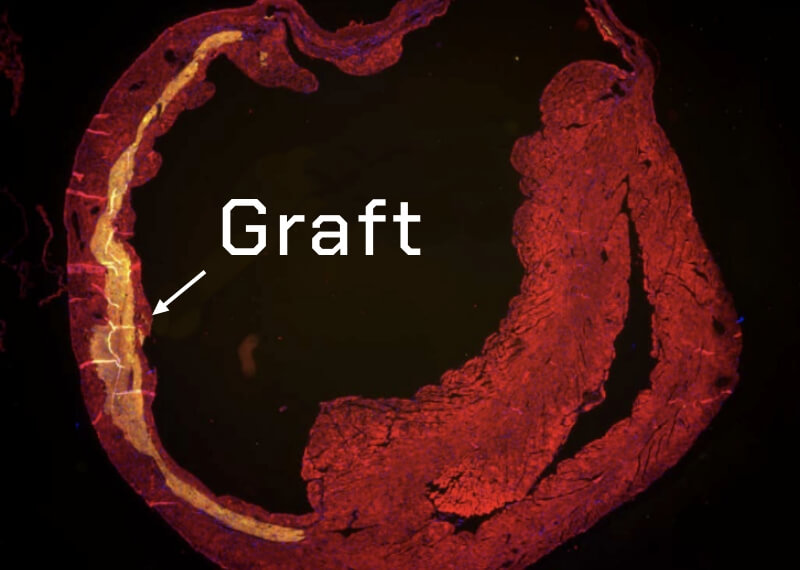
Development of myocardial regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine is critical for patients with currently few treatment options. We are using iPS cells to seek new therapies for this purpose. We aim to create a cardiac regenerative medicine that is therapeutically effective and can serve as a substitute for heart transplantation.
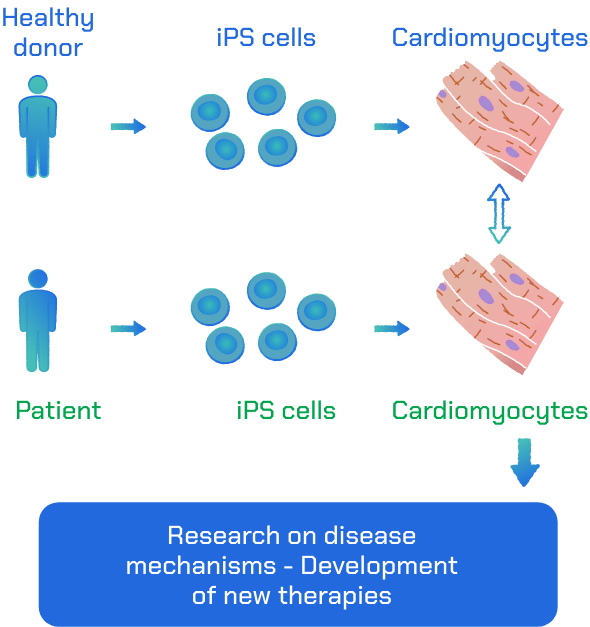
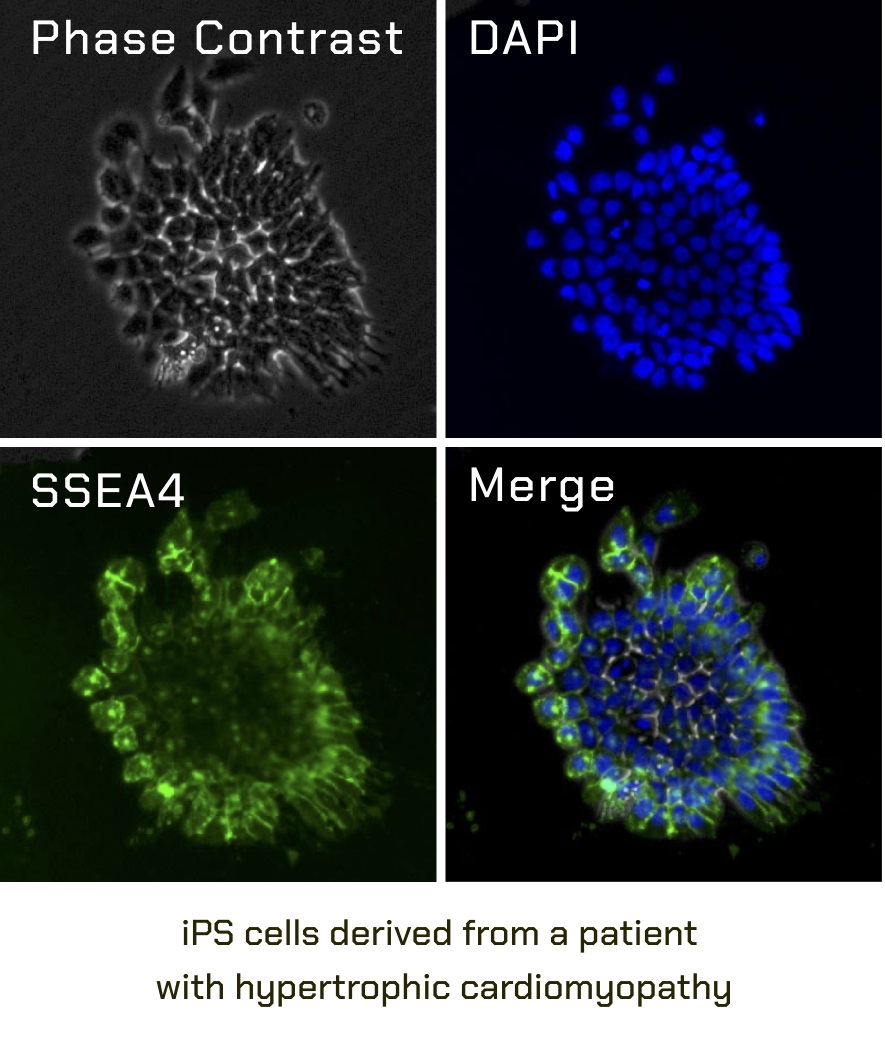
Disease-specific iPS cells
We utilize iPS cells to create disease models that recapitulate disease phenotypes in vitro. Our research primarily focuses on studying cardiac diseases (such as cardiomyopathies and cardiac channelopathies). To further our research, we employ gene editing technology, such as CRISPR/Cas9, to modify iPS cells from diseased patients. We then differentiate the edited and unedited iPS patient cells into the cell type of interest and compare the phenotypes. Our goal is to develop new therapies to treat these diseases.
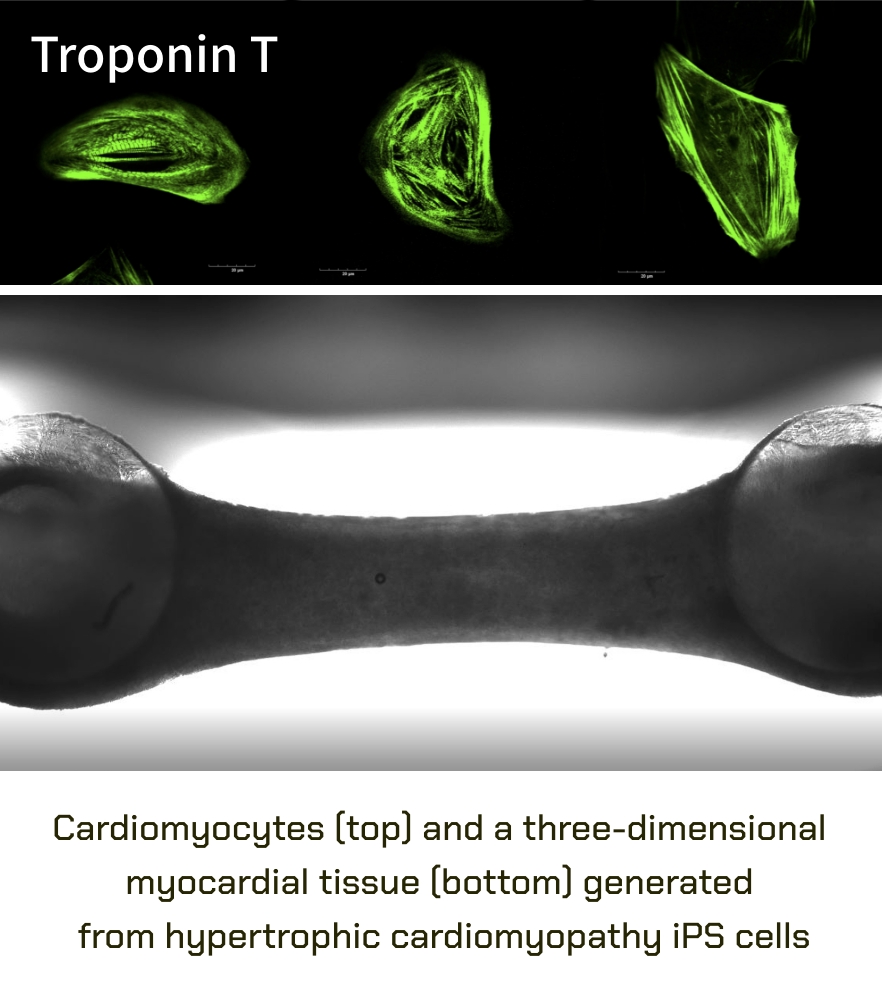
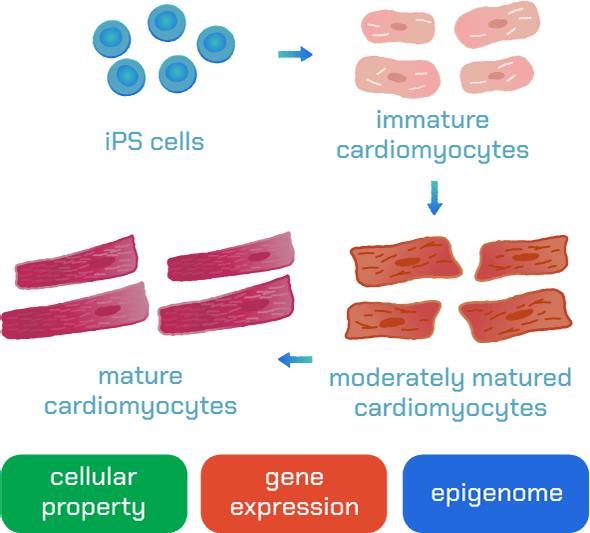
Generation of mature cardiac cells for clinical application
The differentiation of ES/iPS cells to cardiac cells holds tremendous potential for developing new treatments. We are exploring various differentiation protocols, sorting methods, and transplantation techniques to create innovative therapies. In addition to their therapeutic potential, ES/iPS cells also serve as an attractive model for drug discovery and toxicity assays. However, cardiomyocytes describe various subtypes, including pacemaker, atrial, and ventricular cells. Each subtype has its role in the function and disease of the heart. Another factor besides the subtype is the maturity of the cardiomyocytes. Therefore, we investigate protocols that differentiate ES/iPS cells into the proper subtype and maturity to study related diseases and novel therapies.
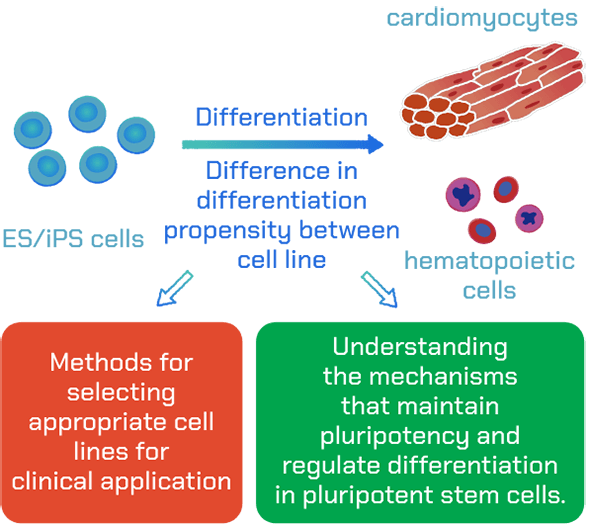
Investigation into mechanisms determining the differentiation capacity of ES/iPS cells
ES/iPS cell clones show variable differentiation capacity to different somatic cell types. To investigate the mechanisms underlying these differences, we are comparing the behavior of these cell lines during differentiation into cardiomyocytes and hematopoietic cells. The goal of this project is to establish iPS cell clones that are suitable for clinical applications.
Research Environment
open lab

Equipments
- Verity Pro
- QuantStudio3/5
- Bioanalyzer
- Cytiva ImageQuant800
- Flux Analyzer XFPro
- BD LSRFortessa
- gentleMACS Octo Dissociator
- Muttiple Electrode Array (Maestro)
Cell culture room

Equipments
- Clean bench
- safety cabinet
- CO2 incubator
- FACS AriaII
- BioX 3D printer
- KEYENCE BZ-X710
- 4D-Nucleofector
others

Equipments
- Patch-clamp system
- Nextseq2000